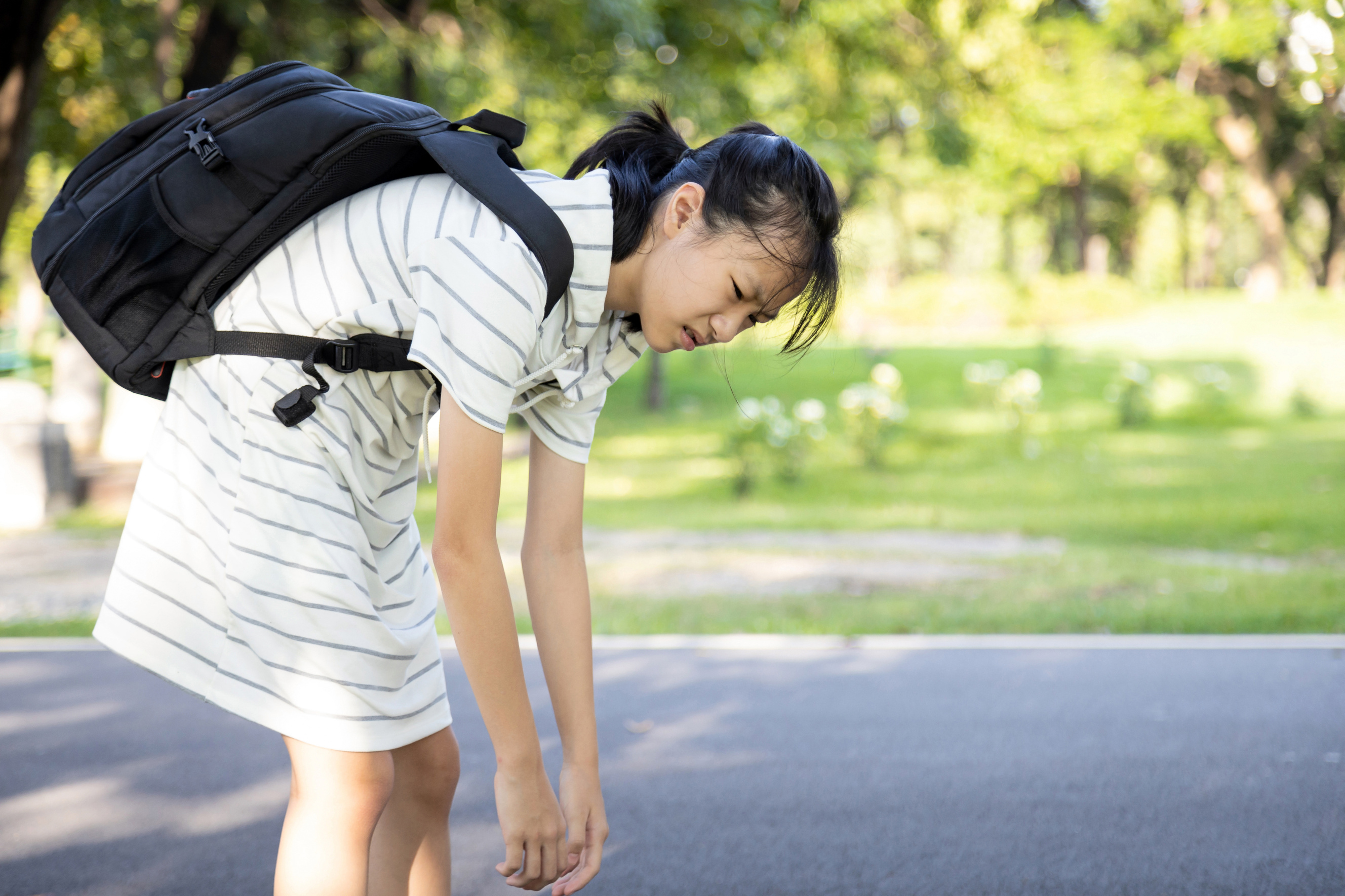
A correlational study: weight of school backpacks and back pain of grade 10 students
12 STEM 3 - TEAM KINULANG SA CANTION

CHAPTER 1: THE RESEARCH PROBLEM

BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
Backpacks are frequently used by students nowadays ever since face-to-face classes started. However, some students do not know that the weight of their backpacks is twice their weight. This can cause bad posture, back pain, or other complications that might distract the students from learning.




STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM

A school backpack is a tool students use to store the things they need to bring to school, and it contains essential things for school, like books, notebooks, and school supplies. However, because of the things carried inside the backpacks, the weight of backpacks can cause back pain since carrying too much of load backpack forces our back to lift it. As a result, the data gathered by this study will help the efficiency of researchers to know the relationship between the weight of school backpacks and the back pain.

General Objective

The study's main objective is to identify the relationship between the weight of school backpacks and back pain. If the heaviness of the backpacks leads to lousy posture under the category of postural health of the Grade 10 Students of Colegio De Sta. Monica de Angat for Academic Year 2022-2023. The researcher aims to identify whether the backpack's weight causes the students to experience back pain that leads to the heaviness that causes harmful effects to their postural health.

Significance of the Study
Students. As the significant benefactor of this study, students will gain advantages in terms of getting additional knowledge about the proper posture they need to attain while carrying a backpack. Teachers. As second parents in school, teachers will acquire additional information on what good posture should be attained by the students. School Administrators. They can provide the knowledge gained from the research to give the proper precautions in carrying backpacks, especially during enrollment or coordinating with parents during parents meeting. The Parents can help them lessen the problem that their children will experience tiredness from the things they carry at school. Future Researchers. This research will benefit other researchers by providing data and facts related to their study. It will serve as a basis that provides opportunities for other researchers to gain learnings, deepen their knowledge, and tap into new ideas.

Scope and Delimitation
In this study, the researchers will look into the relationship between the weight of school backpacks and back pain of Grade 10 Students Academic Year 2022-2023. It aims to determine if their is a significant relationship between the weight of school backpacks and back pain if the weight of school backpacks leads to back pain of Grade 10 students of Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat Academic Year 2022-2023.

The similarities between the study of Pugle (2019) and the present research study is that students should carry at most 10% of their body weight, changing posture and movement patterns from a heavy backpack might raise a child's chance of developing neck and back pain. It can also increase muscular soreness from using a strap with insufficient padding, especially if only one strap, and have a detrimental impact on balance. However, in the present study out of 86 students or 72.3% of the grade 10 department in Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat experienced back pain due to their backpack weight.
Backpack's Weight
Review of Related Literature

Review of Related Studies
Weight of Backpacks
A study by Walicka-CupryV et al. (2015) entitled "Influence of the Weight of a School Backpack on Spinal Curvature in the Sagittal Plane of Seven-Year-Old Children" claimed that children's body is still growing stable during their early school day period. However, this changes when the students begin to attend school, and their time sitting is extended, which can result in disorders of osteogenesis. Furthermore, the pain that the students experience when wearing a backpack that is too heavy is called "backpack syndrome," which includes the following factors, such as abnormal body posture causing headaches, fatigue, and cervical and lumbar pain.
Conceptual Framework
The diagram represents the whole study. Backpacks are carried by learners almost every day. Even so, when misused or weighed too heavily, it can cause serious problems (ABC News, n.d.). Carrying a heavy backpack can result in the deformation of a student's posture. It can also strain children's spines, necks, and shoulders and cause back pain (Phillips, 2021). The child's body will eventually lean forward to balance the extra weight, which may cause the spine to adopt an abnormal position (J World Sports, 2020). Furthermore, when not appropriately addressed or ignored, it can have long-term effects and side effectson the student's body (Hoffman, 2021).
Research Hypothesis
The researchers presented the following hypotheses for their study:
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the back pain of Grade 10 Students of Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the back pain of Grade 10 Students of Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat.
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with mild intensity.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with mild intensity.
Research Hypothesis
The researchers presented the following hypotheses for their study:
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the back pain of Grade 10 Students of Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the back pain of Grade 10 Students of Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat.
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with mild intensity.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with mild intensity.
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with moderate intensity.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with moderate intensity.
H0: There is no significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks and the severity of the students’ back pain with severe intensity.
HA: There is a significant relationship between the weight of the school backpacks
Research Hypothesis
Research Design
This study utilized a correlational design. According to Bhandari (2022), no variables are within the researchers’ direct control or manipulation when using a correlational study design. The intensity and direction of the association between two (or more) variables are also shown in correlation. Additionally, measuring two or more variables is a need for correlational investigations. This research is, therefore, fundamentally quantitative. The researchers can then examine the relationships between the factors. We can anticipate the value of another variable using one variable if two variables are correlated or related to one another. A correlation design is employed in this study to know further the relationship between the weight of backpacks and back pain. The researchers want to determine if the two variables are correlated with each other.
Research Variables
According to Bevans (2022), a variable is an attribute of an object of study in statistical research. Furthermore, because correlational research does not seek to prove a cause-and-effect link (causation), the labels "dependent" and "independent" do not apply. Sometimes a dependent variable is referred to as a criterion variable. A criterion variable is involved in a non-experimental study and serves as the study's outcome. However, the predictor variable forecasts a result (the criterion variable).


According to Brown (2020), the research setting could be physical, social, or experimental. The research setting is where the studies are conducted since this is where most of the problem occurs, which can affect the study's design, data gathered, and how the findings interpret since this study is correlational, Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat provides a good number of students, which can help the researcher to identify whether backpacks' weight relates to the back pain of students and also consider the building where the students go with their bags. Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat (CSMA) is where the researcher decided to conduct the study, specifically in the Blessed Father Marie-Eugene building since the study wants to know the relationship between the weight of school backpacks and the back pain of Grade 10 Students Academic Year 2022-2023. It is located in 3012, Poblacion, Angat, Bulacan.
Research Locale

Research Instrument
According to Collins (2021), a research instrument is a tool that researchers use to obtain, analyze, gather, and measure data relevant to the subject of the study. A research instrument may include a survey, questionnaire, interviews, checklist, and simple .
According to Reed (2023), a weighing scale is a tool or device used to determine the weight of a specific object, including a scale that indicates the weight of the thing. Not only weighing scales are used for objects, but also humans. A questionnaire is a set of questions given to the research participants (Smart Survey, n.d.). The questionnaire is composed of different groups of questions that the researchers can use to gather data from the study participants. Moreover, a survey is used to gather data from a particular group—for example, the grade 10 students of Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat, the respondent of the current study.

Respondents of the Study
According to Kim Omachinski (2017), respondents are individuals who complete a survey or interview for the researcher or contribute data to be examined for the pilot study. Respondents can be of any age, as decided by the scope of the study, and must provide informed consent to participate.The grade 10 students of Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat is the target population of this study comprising one hundred seventy (170) students. Furthermore, the reason the researchers selected them as respondents is that these students are engaged in a variety of academic activities and may be carrying numerous school-related items.


The researchers employed purposive sampling as their sampling method, specifically targeting respondents who met certain criteria, namely individuals who suffer from back pain. The selected participants were chosen based on their responses to a survey questionnaire administered during the initial survey. The researchers assessed both students who experience back pain and those who carry heavy backpacks, as one of the research objectives was to determine whether there is a direct correlation between backpack weight and back pain.
Sampling

The pilot study that the researchers conducted consists of (15) Grade 10 students from Colegio de Sta Monica de Angat for the School Year 2021-2022. The chosen (15) grade 10 students will not participate in the research process. A standardized survey questionnaire is also included. Furthermore, the pilot study’s purpose is to test the reliability of the questionnaires and the presented instruments. It was conducted for the researchers to know the gaps and points of improvement in questionnaires and tools. Additionally, researchers will gain additional knowledge for better revisions and modifications to align with the study.
Pilot Study


A. Seeking Consent, Approval, and Selection of Participants
The researchers obtained permission to gather data for their study. They gave a letter to Ms. Gracia Villamor, the Senior High School Principal, who consented to the research. They also provided a note to Mrs. Francie Castro since the respondents were from the grade 10 of the junior high school department. In addition, letters were distributed to the grade 10 advisers and Mrs. Elizabeth Capistrano, the grade 10 level coordinator, to acquire the students' time schedules and lists. Furthermore, they gave a letter to Mrs. Analiza Marcelo, the school nurse, to borrow a weighing scale as an additional tool for measuring the learners' weight in the study.
Data Collection Procedure

B. Validation
The researchers sought professional validators for their study and had them review the survey questionnaires for reliability, relevance, and clarity. Letters were sent to these experts to request their validation of the questionnaire content. The modified standardized questionnaires were then provided to three experts: a registered physical therapist, a nurse from the Philippine Orthopedic Center, and a science teacher.
C. Measuring Weight of Backpacks of students
The researchers conducted measurements of students' backpacks during the third week of February. These measurements helped the participants provide accurate answers regarding their demographics in the survey. This data collection process was essential in obtaining the appropriate weight values in kilograms for the research items.
Data Collection Procedure

D. Performing a Pilot Study
Prior to conducting the pilot test, consent letters were provided to the advisers of the respective rooms and the selected participants to ensure their willingness to participate. A total of 15 grade 10 students were chosen. The purpose of the pilot test was to gather feedback from the participants and identify areas that needed improvement in order to refine the procedure for the actual survey.
E. Administering a Survey
The researchers showed grade 10 students two videos related to back pain caused by heavy backpacks. An initial survey questionnaire was administered to identify students who experienced back pain and the researchers conducted population sampling from the list of students who reported back pain.
Data Collection Procedure
Data Analysis
The nominal and ordinal data for the level of measurement that was obtained from the survey questionnaires were organized through the use of Microsoft Excel. The researchers analyzed the gathered data to achieve the descriptive statistics: frequency distribution, proportion, percentage, mean rating, and measure of central tendencies.
Moreover, the researchers also analyzed the inferential statistics using the parametric test, specifically the Pearson product-moment coefficient of correlation, to know the relationship between the two variables, and the t-test, specifically tcalc, to compare a sample mean to an accepted value.
In writing this study, the researchers maintained patience and honesty throughout the entire research study. The references from publications, journals, and other studies were adequately cited and acknowledged to increase the study’s credibility. The participants may ensure that the information they supply will be anonymized and used only for research purposes, preventing abuse and leaks to anybody. The researchers considered participant confidentiality when collecting data. The information gathered was not changed or modified in any manner or situation. It will always be in its original format to uphold ethical standards and show respect for everyone who reads or uses the study as a reliable source.
Ethical Considerations
•Frequency Distribution of Student’s Weight of School Backpacks
•Correlation between weight of backpack and back pain with mild intensity
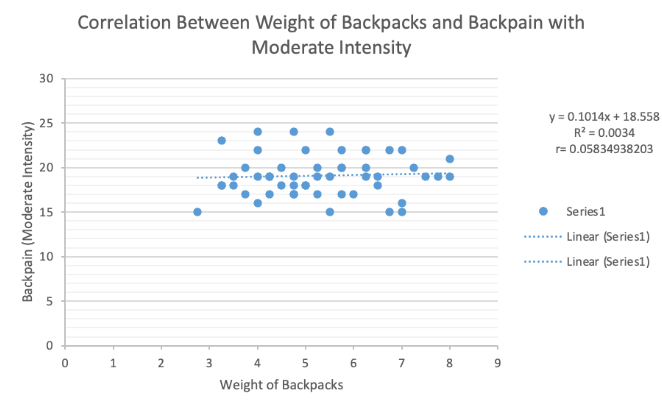
•Correlation Between Weight of School Backpacks and Back Pain with Moderate Intensity
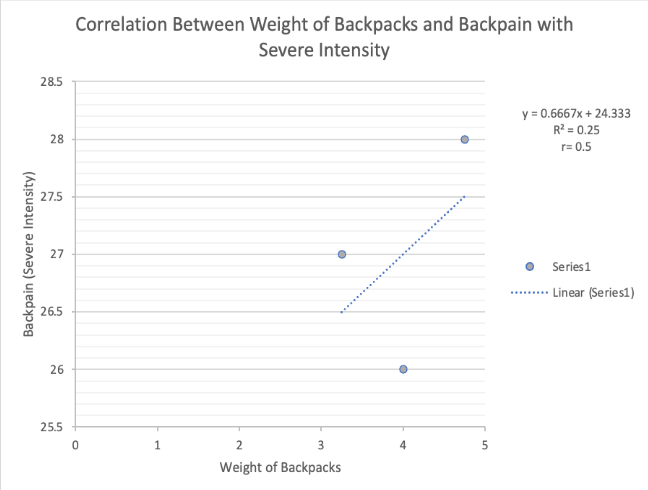
•Correlation Between Weight of School Backpacks and Back Pain with Severe Intensity
•Correlation between weight of backpacks and back pain with different intensity
50
40
30
20
10
0
Item 1
Item 2
Item 3
Item 4
Item 5
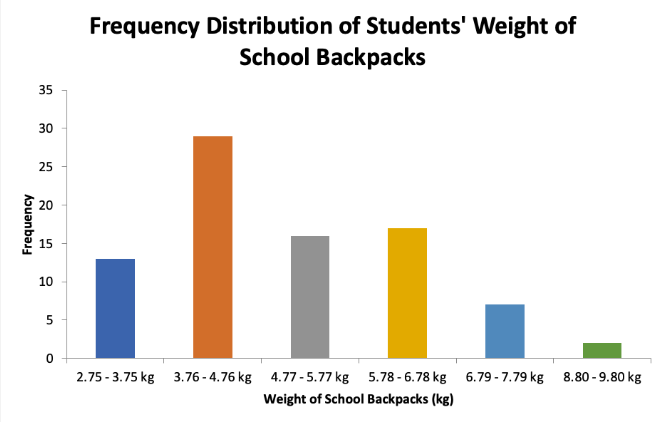
Frequency Distribution of Student’s Weight of School Backpacks (n=84)
As shown in figure, the frequency of student’s school backpacks in the grade 10 department (n=84); thus, it can be inferred from the graph that 29 students have the highest frequency of students who carry 3.76kg to 4.76kg of backpacks, 17 students take 5.78kg to 6.78kg of bags, and 16 students carry 4.77kg to 5.77kg of bags. It can also be inferred that 13 students have 2.75kg to 3.75kg of backpacks, 7 students carry 6.79 to 7.79kg of backpacks, and 2 students carry 8.80kg to 9.80kg of backpacks, which means this has the lowest frequency out of all the intervals.

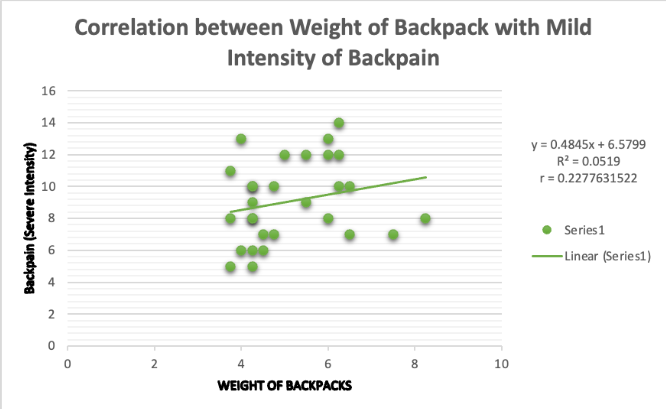
As shown in table figure, weight of school backpack and the severity of school back pain with mild intensity have no significant relationship. Pearson r was calculated, it was equal to 0.2277631522, and was located within the low positive correlation category (0.20-0.40) based on the figure 4.8d. Moreover, the relationship between the two variables was assured by calculating the tcalc. Tcalc is equal to 1.22 that is lower than the critical value which is 2.052.
Correlation between weight of backpack and back pain with mild intensity

Correlation between weight of backpack and back pain with moderate intensity
As shown in figure, the weight of school backpacks and the students who experience back pain with a moderate intensity has no significant relationship. Pearson r was calculated and it is equal to 0.05834938203, and it was located within the slight positive correlation category (0.00-0.20) based on the figure 4.8d. Moreover, the relationship between the two variables was assured by calculating the tcalc. Tcalc is equal to 0.43 that is lower than the critical value which is 2.009.
As shown in figure, the weight of school backpacks and the students who experience back pain with a severe intensity has no significant relationship. Pearson r was calculated and it is equal to 0.53, and it was located within the moderate positive correlation category (0.40-0.70) based on the figure 4.8d. Moreover, the relationship between the two variables was assured by calculating the tcalc. Tcalc is equal to 0.58 that is lower than the critical value which is 12.706.
Correlation between weight of backpack and back pain with severe intensity
Correlation between weight of backpacks and back pain with different intensity
As shown in Figure ,the weight of school backpacks and the students who experience back pain with a different intensity (mild, moderate, severe) has no significant relationship. Pearson r was calculated and it is equal to 0.1804850007, and it was located within the slight positive correlation category (0.0-0.20) based on the figure 4.8d. Moreover, the relationship between the two variables was assured by calculating the tcalc. Tcalc is equal to 1.66 that is lower than the critical value which is 1.96.

CHAPTER 5:Discussions
As shown in the first figure, 5.8 to 6.8 kg of backpacks had the highest frequency with 32 students, 3.6kg to 4.6kg of backpacks had the second highest frequency with 25 students, and 4.7kg to 5.7kg of backpacks had the third highest frequency with 23 students. It can be inferred that half of the students of grade 10 population carry a backpack that is less than or equal to 10% of their body weight. According to Pugle (2019) and the present research study both suggest that students should carry at least 10% of their body weight. However, 72.3% of the grade 10 department in Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat experienced back pain due to their backpack weight.
Weight of Backpacks
Relationship between school backpack weight and back pain
As indicated by the study of Mrozkowiak and Stepien-Słodowska (2021), backpacks' weight may affect the postural alignment of students.
The relationship between weight of backpack and back pain in mild intensity has a weak positive correlation r = 0.22, N = 29. Hence, it can be inferred from the results that weight of backpacks have no significant relationship with the back pain of the students who are experiencing the mild intensity. The data present that although the weight of backpacks and mild intensity of back pain have a positive relationship, their correlation is weak.
The relationship between weight of backpack and back pain in moderate intensity has no correlation, r = 0.05 , N = 52. The value for t-critical in this domain is determined to be 2.009 (df = 50, α = 0.05). Since the t-calc of 0.42 < 2.009, the researchers failed to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, it can be inferred from the results that weight of backpacks have no significant relationship with the back pain of the students who are experiencing the moderate intensity. The data present that although the weight of backpacks and moderate intensity of back pain have a positive relationship, their correlation is very weak.
The relationship between weight of backpack and back pain in severe intensity has no correlation, r = 0.5 , N = 3. The value for t-critical in this domain is determined to be 12.706 (df = 1, α = 0.05). Since the t-calc of 0.57 < 12.706, the researchers failed to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, it can be inferred from the results that weight of backpacks have no significant relationship with the back pain of the students who are experiencing the severe intensity. The data present that although the weight of backpacks and severe intensity of back pain have a positive relationship, their correlation is moderate.


Relationship between school backpack weight and back pain
The relationship between weight of backpack and back pain in severe intensity has no correlation, r = 0.5 , N = 3. The value for t-critical in this domain is determined to be 12.706 (df = 1, α = 0.05). Since the t-calc of 0.57 < 12.706, the researchers failed to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, it can be inferred from the results that weight of backpacks have no significant relationship with the back pain of the students who are experiencing the severe intensity. The data present that although the weight of backpacks and severe intensity of back pain have a positive relationship, their correlation is moderate. In overall weight of backpack and back pain has no correlation, r = 0.18 , N = 84. The value for t-critical in this domain is determined to be 1.960 (df = 82, α = 0.05). Since the t-calc of 1.66 < 1.96, the researchers failed to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, it can be inferred from the results that weight of backpacks have no significant relationship with the back pain of the students who are experiencing the different intensity. The data present that although the weight of backpacks and different intensity of back pain have a positive relationship, their correlation is very weak.
As the findings indicate that the population is experiencing (3) different intensities of back pain (mild, moderate, and severe), it can be concluded that the weight of backpacks and back pain have a positive correlation. Factors are considered why the results gained positive correlation, but statistically speaking, the variables are not significantly correlated. One factor that affects the results is the sample size. It can affect the results of the relationship of the variables; the sample size is small. Moreover, the Hawthorne effect affects the validity of the results wherein the respondents' answers are not truthful because they know that they are being observed.
To conclude our research study, the researchers came up with the results with the made research questions. In research question one, the backpacks weight of the students were measured through weighing scale, and analyzed through microsoft excel. And in research question two, there is no significant relationship between the weight of school backpacks and the different intensities of back pain of Grade 10 students in Colegio de Sta. Monica de Angat.





Recommendation

Based on the results and the study's limitations, the researchers have made several recommendations to the students, teachers, and future researchers. The things the students carry, which comprise the backpack's weight, should be monitored accordingly. The books and notebooks needed per subject should have a limitation, and other miscellaneous materials that the students need to bring. Hence, the researchers recommend that teachers consider planning their activities so that the students bring materials that should be manageable on a single day. Researchers advised the students to carry their backpacks using both shoulders to distribute the weight equally. Moreover, for students experiencing moderate to severe intensity of back pain, going to professionals is advised to avoid any other complications.

Recommendation
Moreover, giving the students the survey face-to-face would be more effective than online questionnaires since the students will answer simultaneously rather than online, where some students need to remember to answer. Furthermore, the researchers recommend that future researchers conduct a longitudinal study with repeated observations of the same variables over a long period. This will be done to gather the same data and determine if the backpack's weight is significantly related to back pain. However, future researchers must consider other variables to determine the other factors related to back pain. Experimental design is also recommended.



A correlational study: weight of school backpacks and back pain of grade 10 students
CONTACT US:

team
kinulang sa canton